Land surveying is crucial in land development, construction, and property management. While many people may be familiar with the term “land surveyor,” their specific duties and responsibilities are often misunderstood.
We will delve into the work of a land surveyor and shed light on the essential tasks they perform to ensure accurate and reliable property surveys. You can also learn about the cost to survey land from Maximum Real Estate Exposure’s comprehensive review.
When you’re done reading, you’ll have a firm understanding of what land surveyors do.
What is a land survey?
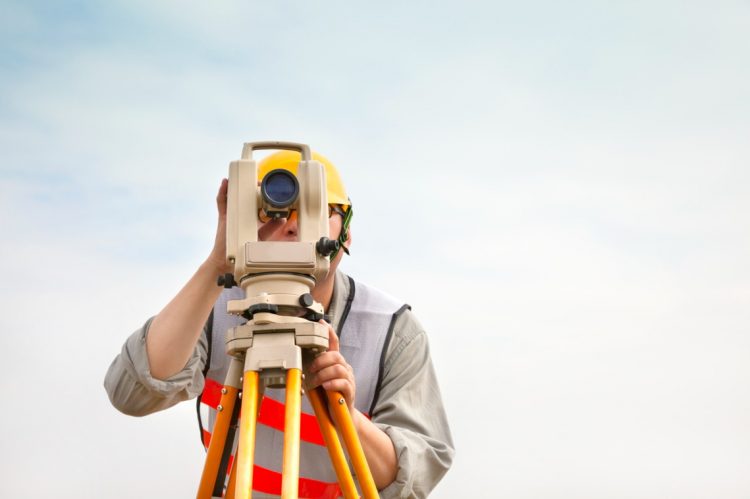
Land surveying determines and maps the earth’s surface’s precise positions, property lines, features and characteristics. It involves using specialized equipment, advanced technologies and expert knowledge to measure and document land, including natural and artificial structures, topographic features and property lines.
The primary objective of a land surveyor is to gather accurate and reliable data to support land development, construction projects, land survey cost and legal disputes.
Roles and responsibilities
Land surveyors are professionals with specialized knowledge and skills in measuring and mapping the Earth’s surface. They are crucial in land development, construction and property management.
Their expertise in boundary surveys, topographic surveys, construction staking, GPS surveys and land development ensures accurate data and precise measurements for legal, engineering and construction purposes.
Here are some of the roles and responsibilities of land surveyors, exploring the vital tasks they perform to ensure the integrity of their work.
Types of property surveys
Boundary surveys
One of the fundamental responsibilities of a land surveyor is to conduct boundary surveys. These surveys precisely locate and mark property lines, corners and boundaries.
Land surveyors determine the exact dimensions and positions of land parcels by employing a combination of historical records, legal documents, physical measurements and geodetic techniques. This information is crucial for resolving property disputes, establishing easements and ensuring compliance with zoning regulations.
There are now several land survey apps that help surveyors complete their work.
Topographic surveys
Land surveyors also perform topographic surveys to represent a land area’s natural and artificial features accurately. By utilizing advanced surveying instruments, such as total stations, GPS receivers and 3D laser scanners, they gather data on the elevation, contours, vegetation, buildings, utilities and other relevant elements on the site.
Topographic surveys are vital in the planning and design of infrastructure projects, including roads, buildings, drainage and septic systems.
Construction staking
During the construction phase of a project, land surveyors play a crucial role in construction staking. They interpret engineering designs and plans to precisely mark the location of proposed structures, utilities, roadways and other project components on the ground.
By ensuring accurate positioning and alignment, surveyors enable contractors to conduct construction activities according to the intended specifications. Construction staking minimizes errors, reduces rework and provides the final product that aligns with the original design.
Global Positioning System (GPS) surveys
With the advent of GPS technology, land surveyors can now access highly accurate positioning data. They utilize GPS receivers and satellite systems to establish precise geodetic control networks and perform surveys with improved accuracy and efficiency.
GPS surveys are particularly beneficial for large-scale projects spanning vast areas, such as highways, pipelines and utility corridors. Surveyors use GPS technology to establish control points, determine elevations and facilitate geospatial data collection.
Land development and subdivisions
Land surveyors are critical in designing and creating new land development and subdivision parcels. They work closely with civil engineers, architects and planners to subdivide more significant properties into smaller lots or tracts while adhering to local zoning and subdivision regulations.
Surveyors determine the boundaries, layout streets, establish easements and ensure the proper distribution of utilities within the developed area. Their expertise ensures efficient land use and compliance with legal requirements.
Geodetic surveys
Land surveyors perform geodetic surveys to accurately measure and establish the three-dimensional positions of points on the Earth’s surface. This includes using advanced techniques such as trilateration and triangulation to determine precise coordinates and elevations.
Geodetic surveys are crucial for large-scale mapping projects, geospatial data collection and establishing reference networks.
Hydrographic surveys
Land surveyors specializing in hydrographic surveys work in marine or freshwater environments to map and measure the physical features and contours of bodies of water. They use specialized equipment, such as sonar systems and echo sounders, to gather data on underwater topography, water depths and submerged structures.
Hydrographic surveys are essential for navigation, dredging operations, coastal engineering and environmental assessments.
Legal and cadastral surveys
Land surveyors often provide expertise in legal and cadastral surveys, which involve determining property rights, land ownership and establishing cadastral systems. They work closely with lawyers, land registries and government agencies to conduct surveys that accurately define and document land parcels.
Legal and cadastral surveys are critical for property transactions, land titling, land administration and resolving land disputes such as property encroachments.
Monitoring surveys
Land surveyors perform monitoring surveys to track changes in the physical attributes of land, structures, or infrastructure over time. They use precise measurements like deformation and settlement monitoring to detect and quantify movements, subsidence or other changes.
Monitoring surveys are essential for ensuring the safety and stability of buildings, dams, bridges and other critical infrastructure.
GIS (Geographic Information System) and mapping
Land surveyors often use GIS technology to collect, analyze and manage spatial data. They use specialized software to integrate survey data with other geographic data, creating detailed maps, digital models and databases.
GIS and mapping are essential for urban planning, land management, environmental assessments and decision-making processes.
Final thoughts
Land surveyors are highly skilled professionals who contribute significantly to the planning, developing and managing infrastructure.
Through their meticulous work, they provide accurate data and measurements that are vital for legal, engineering and construction purposes.
Whether determining property boundaries, conducting topographic surveys or assisting in construction staking, land surveyors are pivotal in ensuring precise and reliable information about the land.
Bill Gassett is a nationally recognized real estate leader who has been helping people buy and sell MetroWest Massachusetts real estate for the past 35 years.